
- HOW TO INSTALL GITLAB DOCKER HOW TO
- HOW TO INSTALL GITLAB DOCKER DRIVER
- HOW TO INSTALL GITLAB DOCKER FULL
docker-volumes /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock Register GitLab Runner from the command line to use docker and share /var/run/docker.sock: sudo gitlab-ci-multi-runner register -n \ The third approach is to bind-mount /var/run/docker.sock into the container so that docker is available in the context of that image. To use a different driver, see Using the overlayfs driver.Īn example project using this approach can be found here. By default, docker:dind uses -storage-driver vfs which is the slowest form offered.But this also means jobs can be slower because there's no caching of layers.
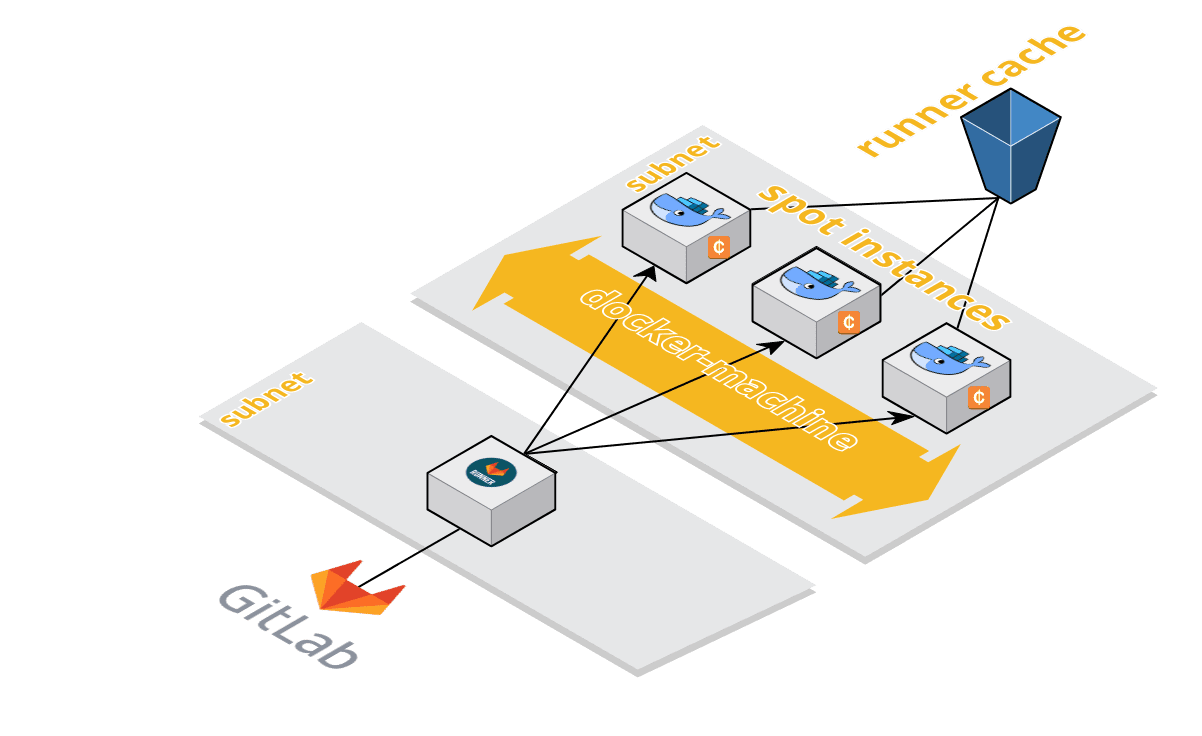
Concurrent jobs work fine because every build gets it's own instance of Docker engine so they won't conflict with each other. When using docker-in-docker, each job is in a clean environment without the past history.

For more information, check out the official Docker documentation on Runtime privilege and Linux capabilities.
HOW TO INSTALL GITLAB DOCKER DRIVER
# When using dind, it's wise to use the overlayfs driver for # improved performance. You can now use docker in the build script (note the inclusion of the docker:dind service): image: docker:latest The above command will create a config.toml entry similar to this: ] If you want to use docker-in-docker mode, you always have to use privileged = true in your Docker containers. Notice that it's using the privileged mode to start the build and service containers. The above command will register a new Runner to use the special docker:latest image which is provided by Docker. Register GitLab Runner from the command line to use docker and privileged mode: sudo gitlab-ci-multi-runner register -n \ The second approach is to use the special docker-in-docker (dind) Docker image with all tools installed ( docker and docker-compose) and run the job script in context of that image in privileged mode. For more information please read On Docker security: docker group considered harmful.
HOW TO INSTALL GITLAB DOCKER FULL
HOW TO INSTALL GITLAB DOCKER HOW TO
registration-token REGISTRATION_TOKEN \įor more information how to install Docker Engine on different systems checkout the Supported installations.Īdd gitlab-runner user to docker group: sudo usermod -aG docker gitlab-runner GitLab Runner then executes job scripts as the gitlab-runner user.ĭuring GitLab Runner installation select shell as method of executing job scripts or use command: sudo gitlab-ci-multi-runner register -n \ The simplest approach is to install GitLab Runner in shell execution mode. There are three methods to enable the use of docker build and docker run during jobs each with their own tradeoffs.
This requires special configuration of GitLab Runner to enable docker support during jobs. $ docker tag my-image my-registry:5000/my-image $ docker run my-docker-image /script/to/run/tests It's also useful when your application already has the Dockerfile that can be used to create and test an image: $ docker build -t my-image dockerfiles/


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
